*26-year-old pregnant female.


What is the most likely diagnosis?
Answer
Answer: Congenital diaphragmatic hernia
Case Discussion:
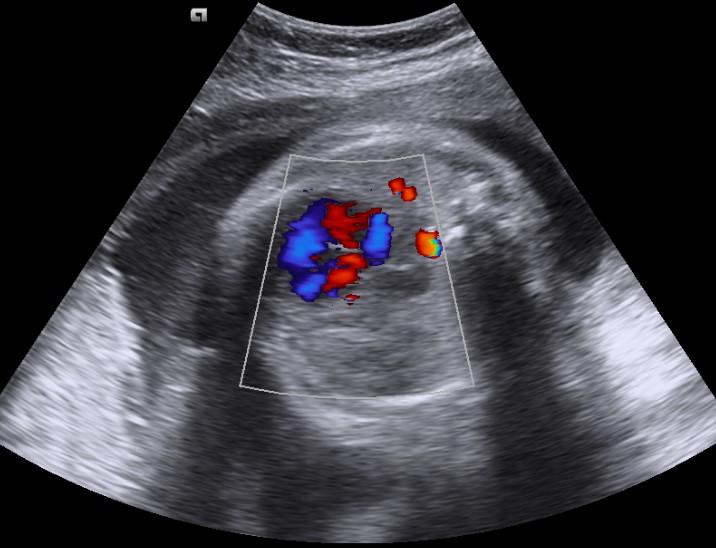
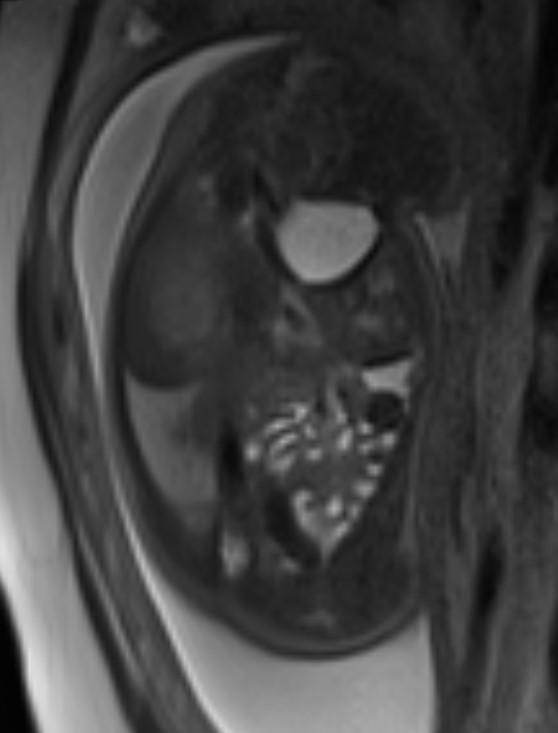
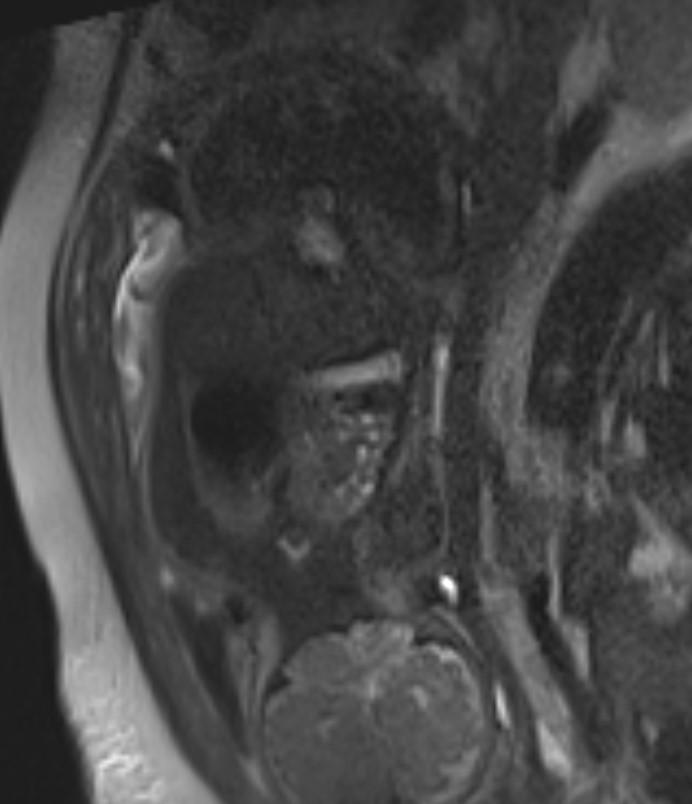
Obstetric ultrasound and MR images showed the stomach, small bowel and heart within the thorax. The heart is displaced to the fetus right.


Congenital diaphragmatic herniation is a small proportion of all diaphragmatic hernia.
Classification of congenital diaphragmatic hernias (1):
• Bochdalek hernia: most common, located posteriorly and typically presents earlier (in infancy)
• Morgagni hernia: less common, smaller, located anteriorly and presents later
Sonographic findings (2, 3):
• polyhydramnios
• cardiomediastinal shift
• inability to demonstrate the normal stomach bubble
• absent bowel loops in the abdomen
• intra-thoracic herniation of the liver
• left-sided CDH
stomach and small bowel (echo-free) at the same transverse level as the heart on four-chamber view
stomach and small bowel superior to the inferior margin of the scapula
leftward displacement of the gallbladder
• right-sided CDH
colour Doppler study
leftward bowing of the umbilical segment of the portal vein
portal branches to the lateral segment of the left hepatic lobe coursing towards or above the diaphragm
gallbladder present above diaphragm
echodense space between the left heart border and stomach representing the left hepatic lobe
Fetal MRI findings (4, 5):
• T1-weighted fast field echo (FFE)
o liver appears moderately hyperintense
• T2-weighted half-fourier acquisition single-shot turbo spin echo (HASTE)
o lungs appear hyperintense (composed primarily of water) while heart, mediastinum and liver appear hypointense
Differential diagnosis
• congenital pulmonary airway malformation
• hybrid lesion
• pulmonary sequestration
References:
1- Callen PW. Ultrasonography in obstetrics and gynecology. W B Saunders Co. 2000
7. Chinn DH, Filly RA, Callen PW et-al. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia diagnosed prenatally by ultrasound. Radiology. 1983;148 (1): 119-23.
8. Taylor GA, Atalabi OM, Estroff JA. Imaging of congenital diaphragmatic hernias. Pediatr Radiol. 2009;39 (1): 1-16. doi:10.1007/s00247-008-0917-7 – Pubmed citation
12. Mehollin-Ray AR, Cassady CI, Cass DL et-al. Fetal MR imaging of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Radiographics. 2012;32 (4): 1067-84.
13. Victoria T, Danzer E, Adzick NS. Use of ultrasound and MRI for evaluation of lung volumes in fetuses with isolated left congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Semin. Pediatr. Surg. 2013;22 (1): 30-6.
