*Newborn with respiratory distress. Failure to pass NG tube.




What is the most likely diagnosis?
Answer
Answer: Choanal atresia
Case Discussion:
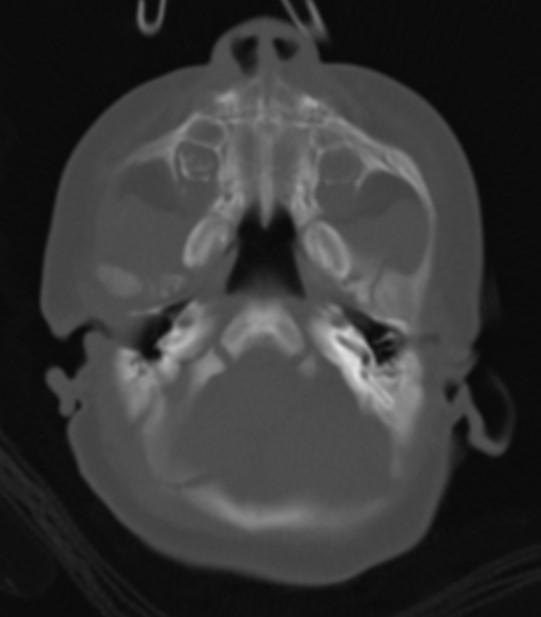
CT images showed bilateral osseous choanal atresia (arrows) and retention of secretions.

Choanal atresia is a narrowing or blockage of the nasal passage by abnormal bony or soft tissue. It is a congenital disorder and can be unilateral or bilateral.
• 90 % of cases are osseous (10 % membranous)
• 2/3 are unilateral (1/3 bilateral)
Diagnosis is confirmed by radiological imaging, usually CT scan.
• can demonstrate a uni or bilateral posterior nasal narrowing with an obstruction
• airway less than 3 mm at the level of the pterygoid plates in the axial plane
• Retention of secretions
• can demonstrate thickening of the vomer
• medial bowing of posterior maxillary sinus
References:
1. Hengerer AS, Brickman TM, Jeyakumar A. Choanal atresia: embryologic analysis and evolution of treatment, a 30-year experience. Laryngoscope. 2008;118 (5): 862-6.
2. Szeremeta W, Parikh TD, Widelitz JS. Congenital nasal malformations. Otolaryngol. Clin. North Am. 2007;40 (1): 97-112.
3. Tadmor R, Ravid M, Millet D et-al. Computed tomographic demonstration of choanal atresia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 5 (6): 743-5.
