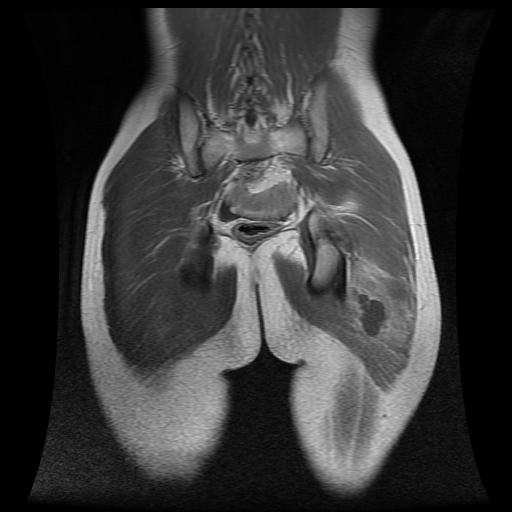
*14 year-old male with fever, left buttock pain and swelling.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
1. Gluteal abscess
2. Gluteal haematoma
3. Gluteal mass
4. Scar formation
Answer
Answer: Gluteal abscess secondary to injection
Case Discussion:
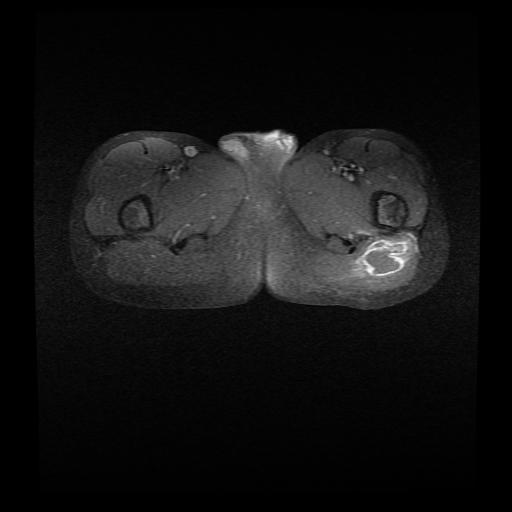
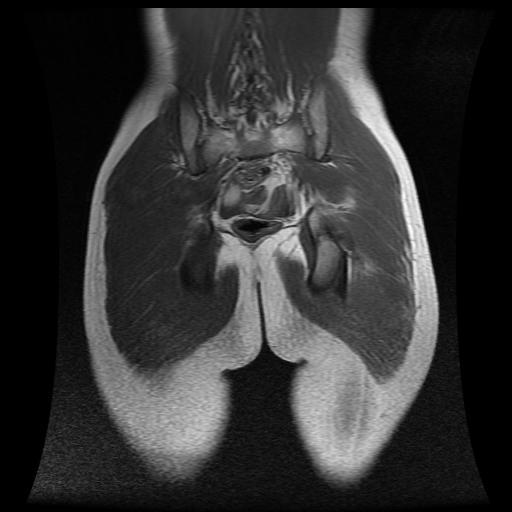
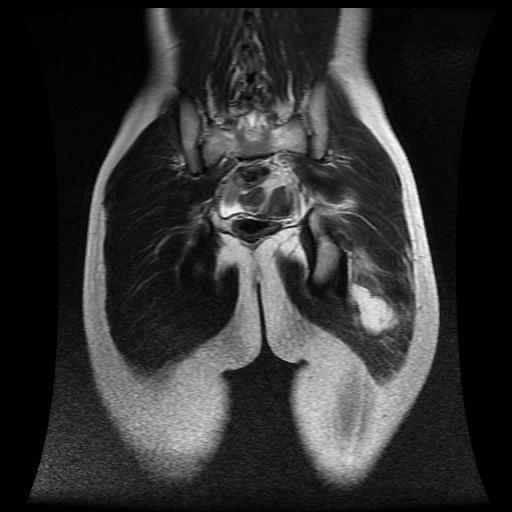
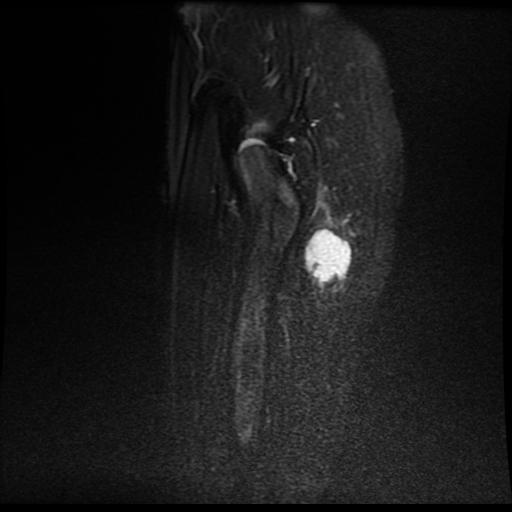
MRI sections demonstrate gluteal abscess secondary to injection. They demonstrate fluid collection with enhanced wall in the left gluteus muscles.
Gluteal abscess is described as collection of pus in the gluteal region. Gluteal abscess is generally related to intra-muscular injections although other causes have been documented. The incidence of gluteal abscess from these injections range from 0.4 to 19.3% (1). Other complications reported include; induration, erythema, wheal formation, persistent local pain, hematoma, bleeding, subcutaneous nodularity, paralysis from infiltration of the sciatic nerve, distal ischemia due to intra-arterial injection of epinephrine, scar formation, muscle fibrosis (2, 3).
MRI has an major role in detection and characterization of muscular signal changes secondary to different pathologic conditions. MRI is useful in the evaluation of anatomical detail and muscles morphology. T1WI is the best adequate for the evaluation of anatomy and also provide presence of subacute hemorrhage and muscle atrophy. T2WI is necessary to detect edema and pathology. Contrast-enhanced T1WI are helpful to differ solid lesions and cystic lesions. DWI is useful to detect subtle muscular edema and to characterize mass like lesions.
References:
1. Greenblatt DJ, Allen MD. Intramuscular injection site complications JAMA 1978; 240:542-4
2. Beecroft PC , Redick S .Possible complications of intramuscular injections in the pediatric unit. Pediat Nurs 1989; 15:333-6
3. VanHook r R , Vandevelde AG. Gas gangrene after intramuscular injection of epinephrine. Ann Intern Med 1975; 83:669-70
