*50-year-old male present with headache.
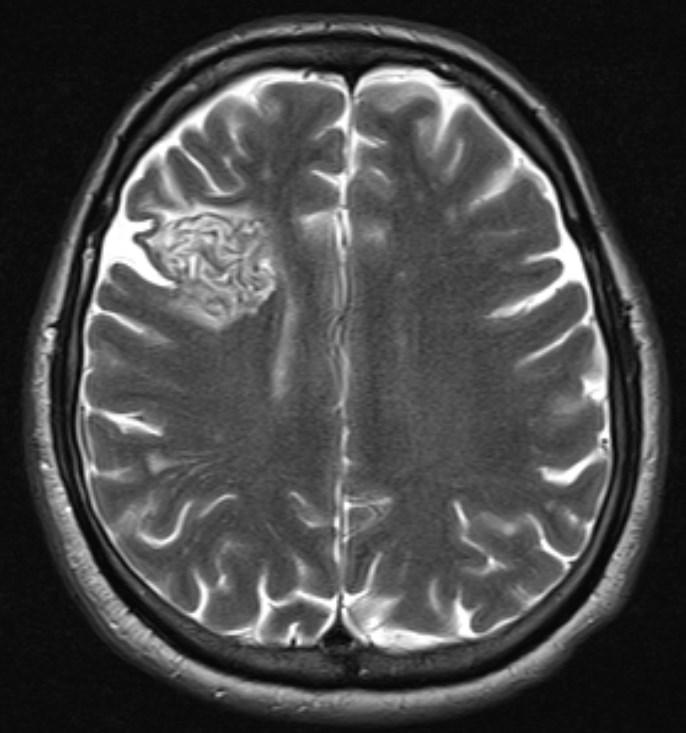
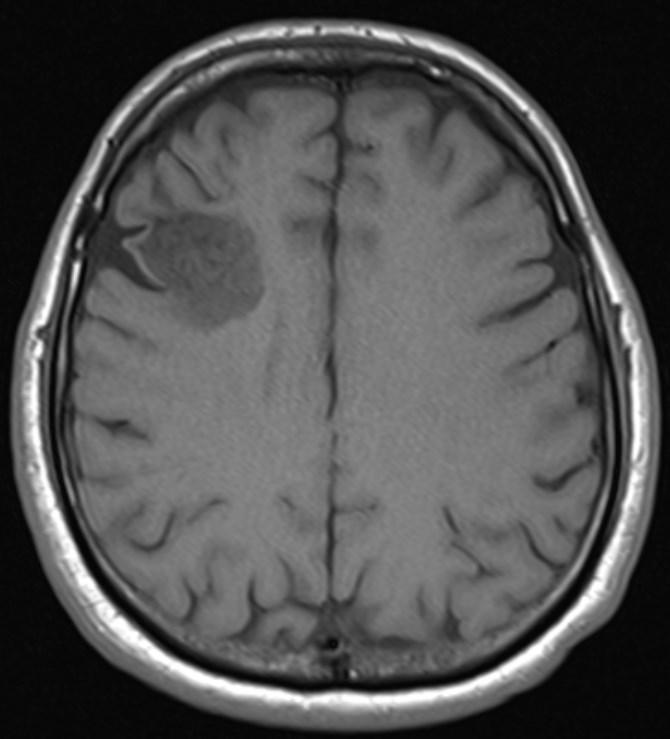
What is the most likely diagnosis?
Answer
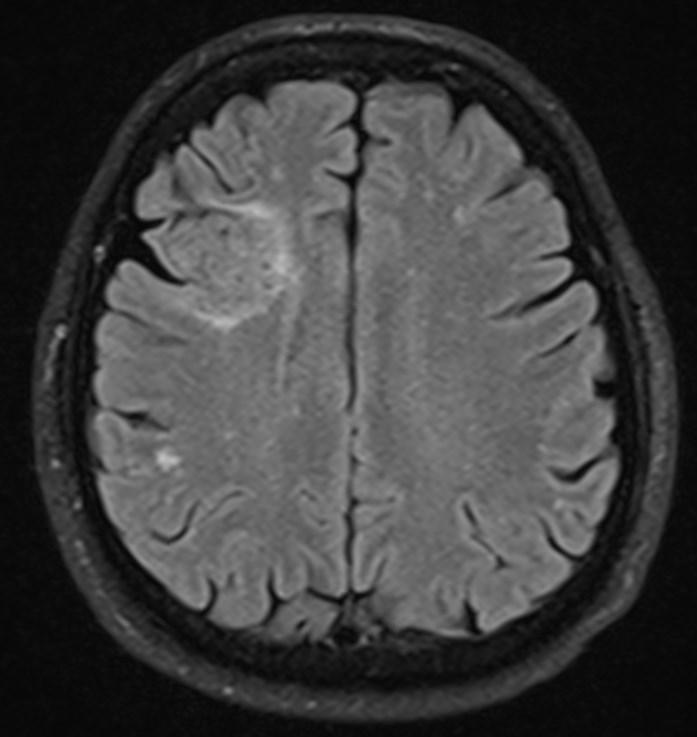
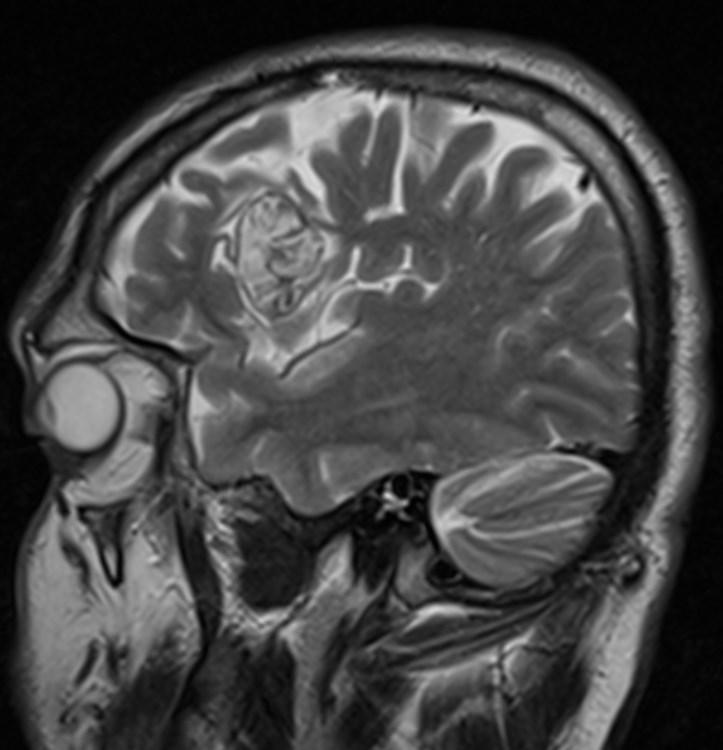
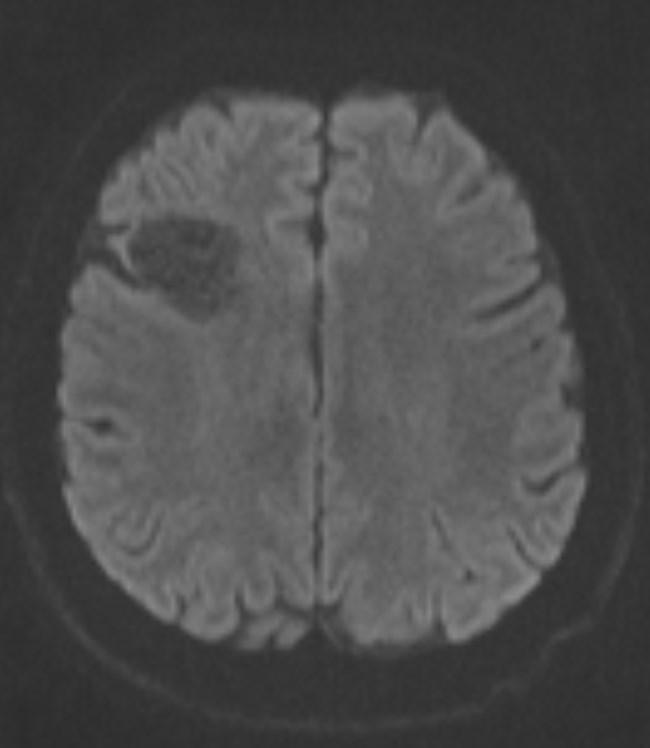
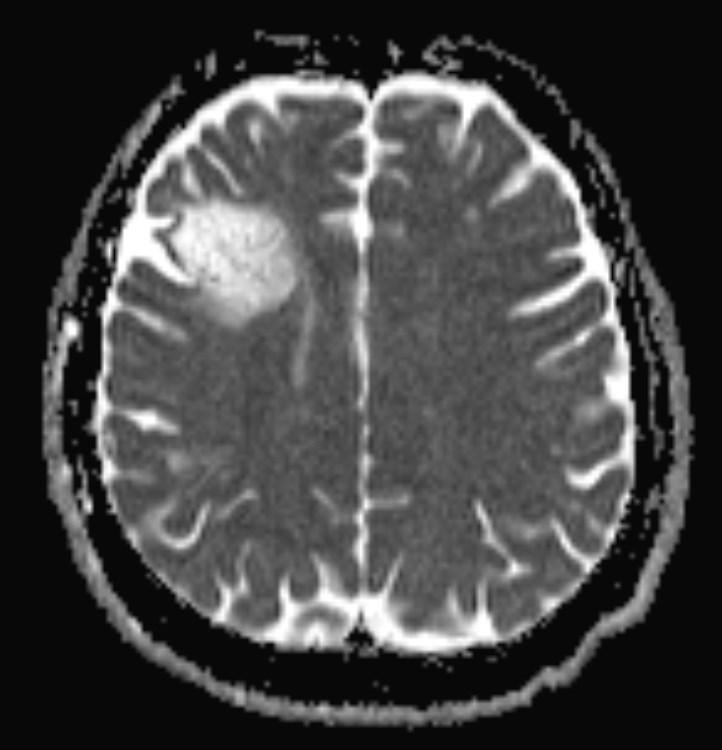
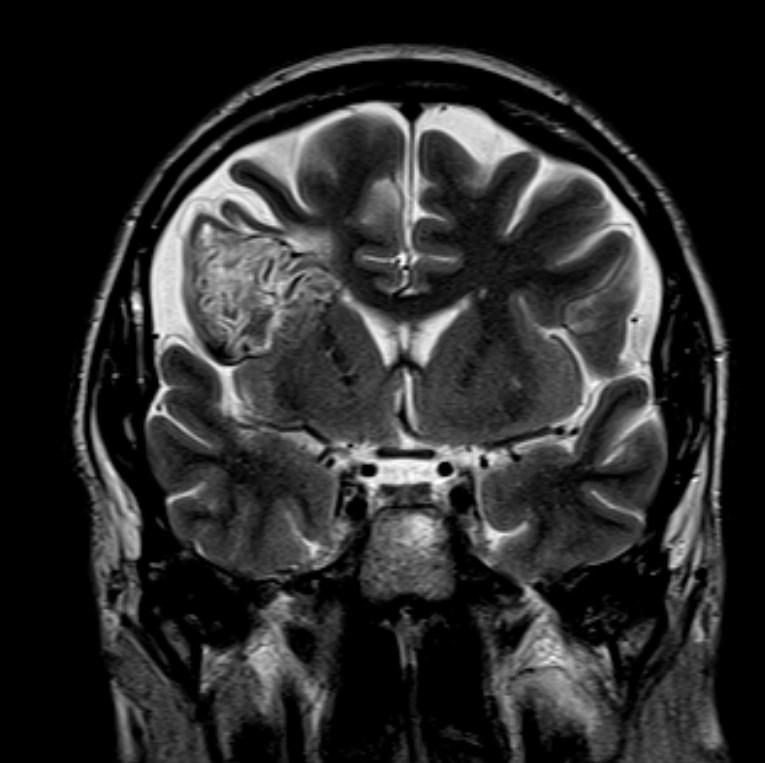
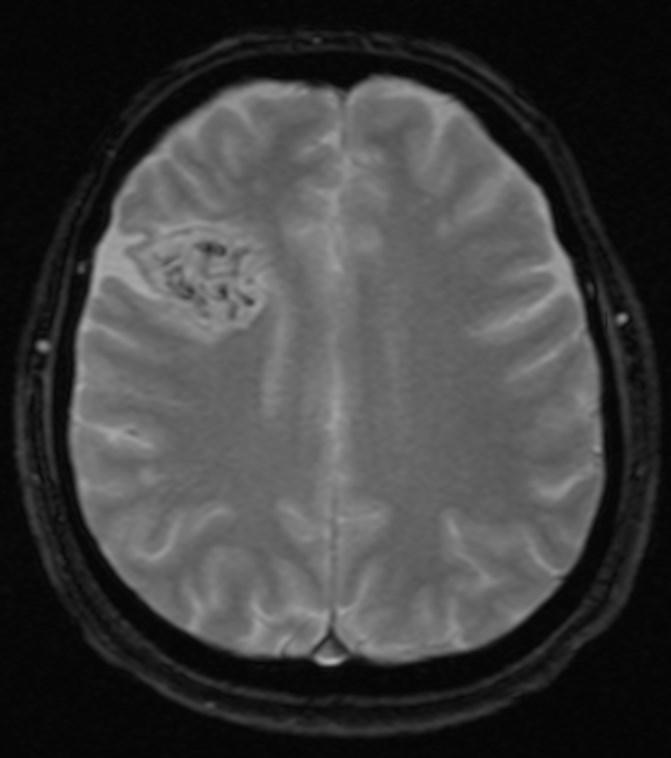
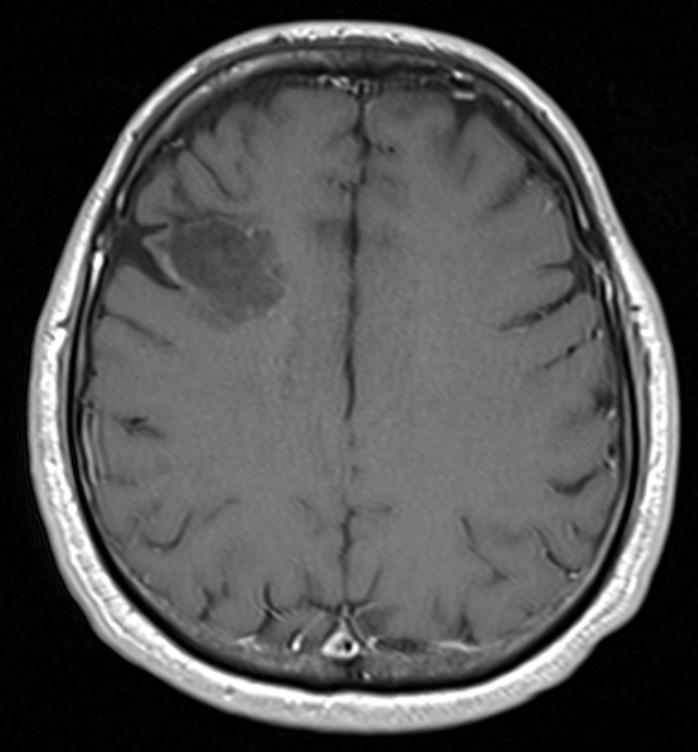
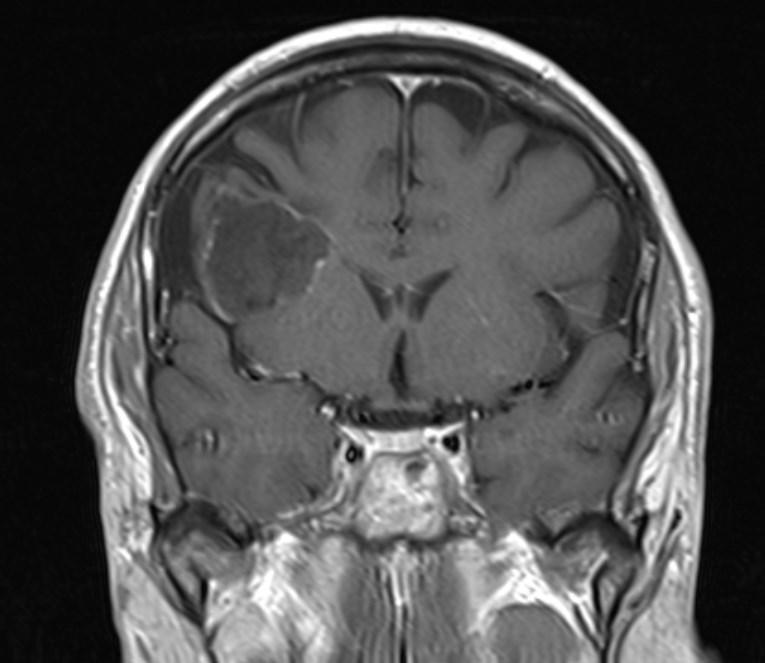
Answer: Primary hydatid cyst of right frontal lobe.
Case Discussion:
MR images revealed Gharbi type V hydatid cysts in right frontal lobe.
Brain involvement with hydatid disease occurs in 1–2% of all Echinococcus granulosus infections. Primary cerebral hydatid disease is a rare clinical entity.
Hydatid disease is a parasitic disease caused by Echinococcosis Granulosus, which may affect the whole body. It most often spreads to the liver and lungs (1,2). Radiological imaging and serological testing are generally used diagnostic techniques. Ultrasonography is the first choice in radiological imaging for the diagnosis of hydatid cyst. However, CT and MRI can be used for differential diagnosis or in classification. Ultrasonography images of hydatid cysts vary according to the stage of maturation (3).
Gharbi classified hydatid cyst ultrasonographic images into 5 types: Type 1, walled, unilocular, anechoic; type 2, separated membranes; type 3, multisepta, daughter vesicles; type 4, heterogenic, hypo-hyperechogenic; type 5, calcification of a section of the wall or completely calcified (4). The cysts characteristically have three components: Pericyst, Exocyst, and Endocyst.
References:
1. Ammann RW, Eckert J. Cestodes: Echinococcus. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 1996;25(3):655-89.
2. WHO Informal Working Group on Echinococcosis. Guidelines for treatment of cystic and alveolar echinococcosis in humans. Bull World Health Organ 1996;74(3):231-42.
3. Caremani M, Lapini L, Caremani D, Occhini U. Sonographic diagnosis of hydatidosis: the sign of the cyst wall. Eur J Ultrasound 2003;16(3):217-23.
4. Gharbi HA, Hassine W, Brauner MW, Dupuch K. Ultrasound examination of the hydatic liver. Radiology 1981;139(2):459-63.
