*65-year-old male with with left-sided hemiparesis.


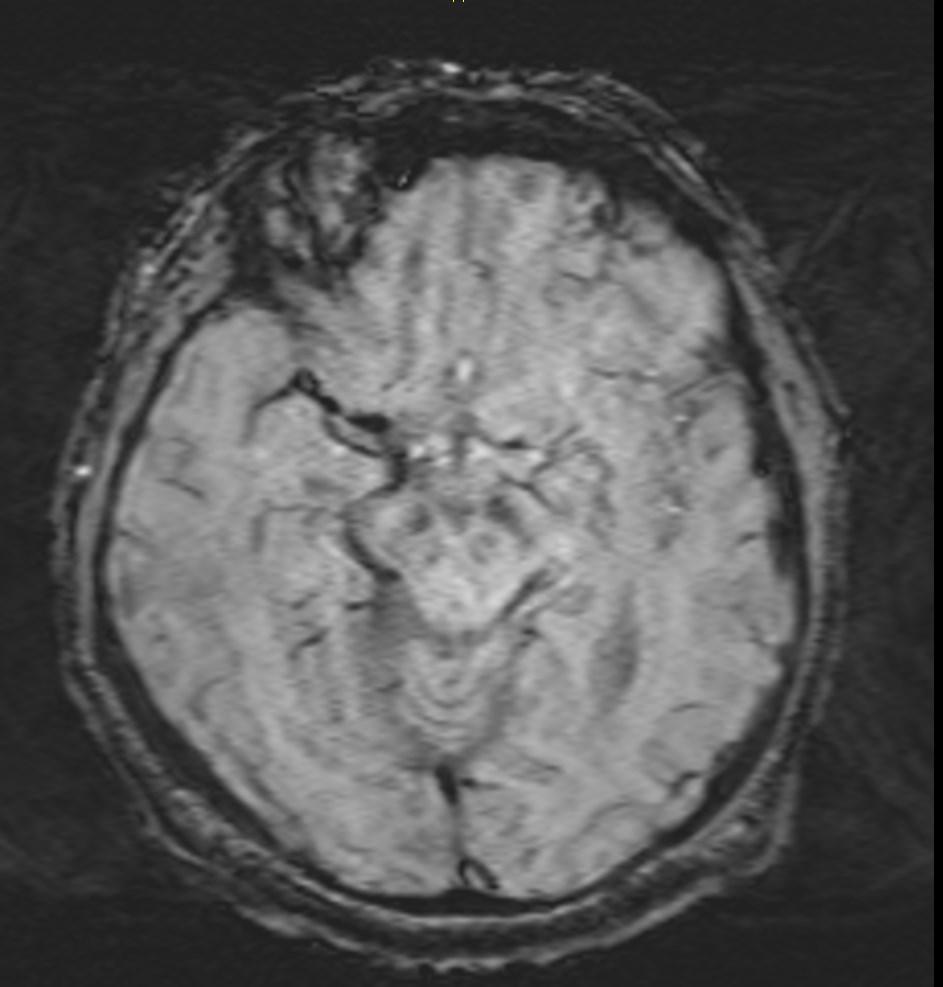
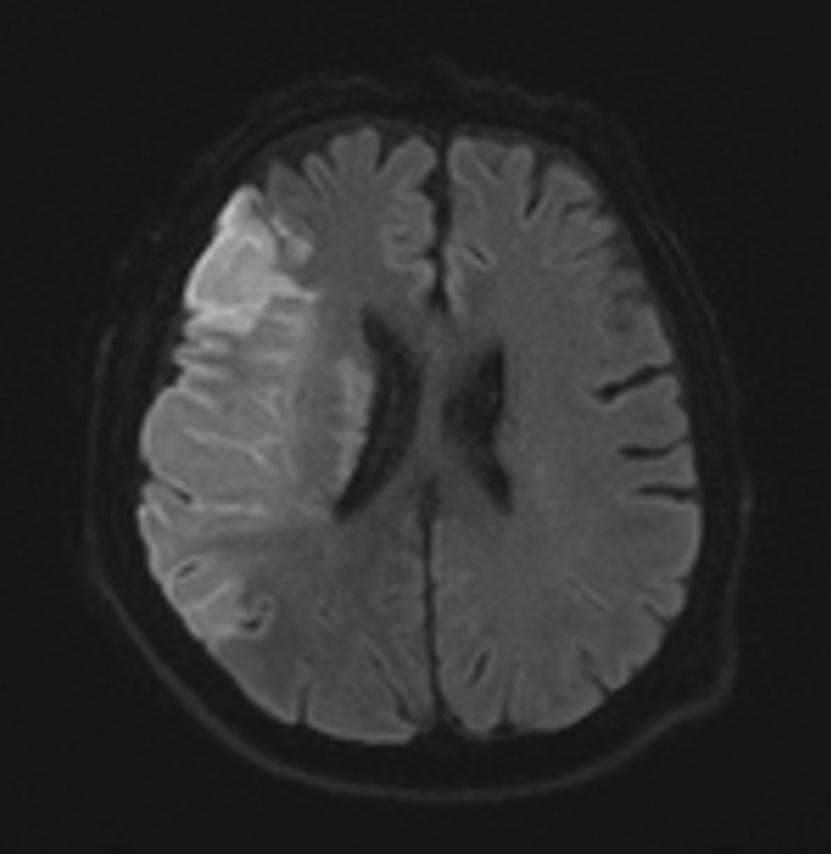
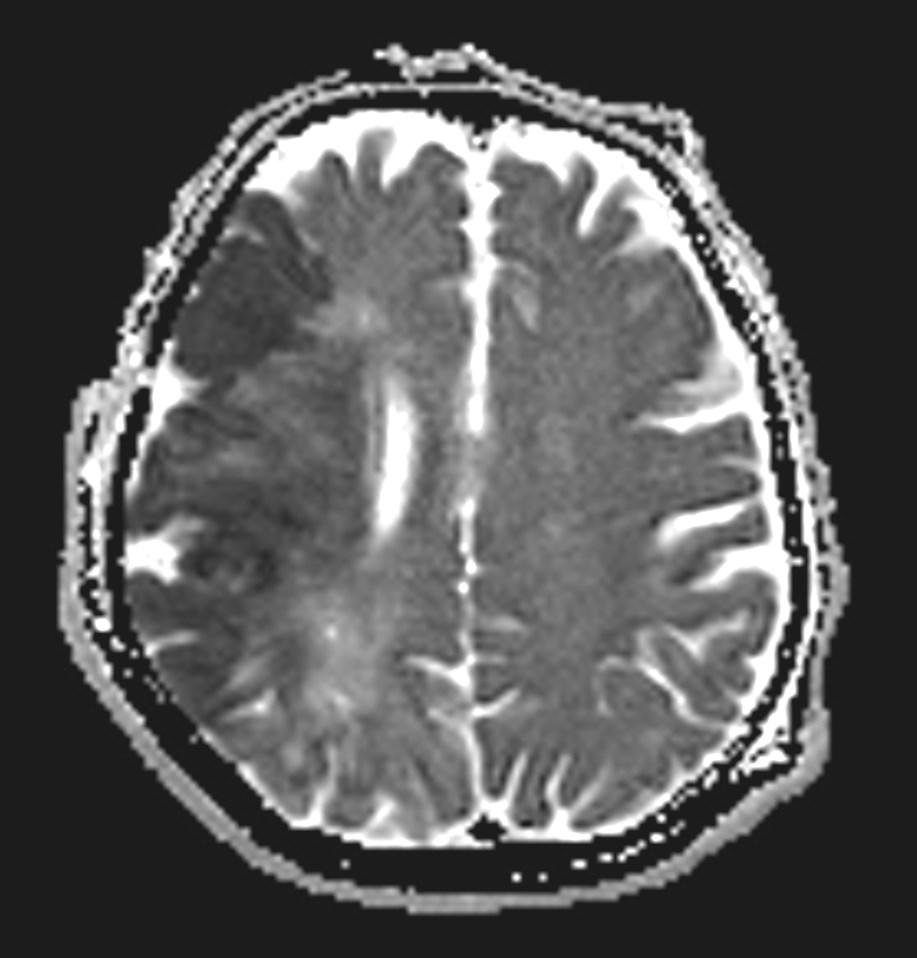
What is the most likely diagnosis?
Answer
Answer: Acute right MCA territory infarct
Case Discussion:
CT and MRI images showing the hyperdense middle cerebral artery sign and low attenuation change in the surrounding brain.
The middle cerebral artery territory is the most commonly affected territory in a cerebral infarction, due to thromboembolism.
Clinical presentation include contralateral hemiparesis, contralateral hemisensory loss, hemianopia, and aphasia.
The earliest finding of middle cerebral artery occlusion on CT is hyperdense middle cerebral artery sign.
Early parenchymal signs include subtle blurring, decreased attenuation and swelling of the grey-white matter junction of affected regions.
References:
1. Moulin T, Cattin F, Crépin-leblond T et-al. Early CT signs in acute middle cerebral artery infarction: predictive value for subsequent infarct locations and outcome.Neurology.1996;47 (2):366-75.
2. Pressman BD, Tourje EJ, Thompson JR. An early CT sign of ischemic infarction: increased density in a cerebral artery. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987;149 (3): 583-6.
3. Nakano S, Iseda T, Kawano H et-al. Correlation of early CT signs in the deep middle cerebral artery territories with angiographically confirmed site of arterial occlusion. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001;22 (4): 654-9.
